Understanding luminous efficacy and strategies for improvement
Understanding luminous efficacy and strategies for improvement
Introduction
We usually divide light source technology into three generations: the first generation is thermal radiation light sources, the second generation is gas discharge light sources, and the third generation is solid-state light sources, namely LEDs. Since 2008, LEDs have gradually become popular in various places, mainly because LED technology has many advantages. First of all, the most significant advantage of LED lights is their high energy efficiency. Compared with traditional incandescent lamps, LED white light efficiency is more than five times higher. LED lamps can convert 40%-50% of electrical energy into light energy, while traditional incandescent lamps only convert 10% or even less energy into light. This clearly shows that LEDs greatly reduce energy waste and have a lower impact on the environment by reducing human energy demand. Additionally, LED lights have several advantages such as long lifespan, a wide range of colors, no pollution from toxic substances, quick start, compact size, and convenient design. These factors contribute to the increasing prevalence of LEDs in everyday human life. This article focuses on how to improve the luminous efficacy of LED lights because we believe that this is the most important feature of LEDs and enhancing their luminous efficacy will enable their broader usage.”
What’s luminous efficacy?
Luminous efficacy is the measure of how efficiently a light source produces visible light. It is defined as the ratio of luminous flux (measured in lumens) to power (measured in watts – watts to lumens for LED lights. ), expressed in lumens per watt (lm/W). High luminous efficacy of luminaires means that, under a given power input, more visible light output and better lighting effects can be obtained. Therefore, the luminous efficacy of luminaires is an important indicator for evaluating the performance and efficiency of a lighting device, reflecting the energy-saving potential and lighting quality of a lighting system. In the field of lighting, “light efficacy of LEDs” and “light efficacy of luminaires” are two related but distinct concepts.
The light efficacy of LEDs refers to the efficiency with which individual light sources, such as LED chips, convert input electrical energy into visible light. It indicates the brightness or luminous flux produced by the LEDs per unit energy consumption and is typically expressed in lumens per watt (lm/W). Higher light efficacy indicates brighter light produced by the LEDs and greater energy efficiency, allowing for higher light output under the same power.
On the other hand, the light efficacy of luminaires refers to the overall energy utilization efficiency of the entire lighting device, including LEDs and other auxiliary components such as reflectors, lenses, and radiators. The light efficacy of luminaires encompasses the efficiency of the lamp beads and is influenced by various factors, including the efficiency of the LEDs themselves, optical design, heat dissipation design, and LED driver circuit(efficiency). Addressing these factors can improve the light efficacy of luminaires.
Benefits of high luminous efficacy
LED lighting has many advantages due to its high luminous efficacy. Here are some of the key benefits:
Energy-saving and high efficiency: LED luminaires with high luminous efficacy means they can produce more brightness with the same energy consumption. Compared to traditional lighting technologies, LED luminaires achieve higher energy utilization, resulting in electricity savings. This is particularly significant for urban lighting systems as it reduces energy expenses and the demand for electricity resources.
Long lifespan and durability: High luminous efficacy means that LED luminaires generate relatively low heat while meeting lighting requirements, which helps reduce aging and damage to LED chips. The long lifespan of LED luminaires translates to less maintenance and lower replacement costs, making them particularly suitable for large-scale lighting systems such as road lighting and urban area lighting.
Cost-saving: Due to the high luminous efficacy of LED luminaires, fewer units are required for the same lighting demands. This means cost savings in terms of installation and maintenance, reducing the consumption of manpower and resources. The long lifespan of LED luminaires also reduces the frequency and cost of replacement.
Environmental-friendly: High-efficiency LED luminaires reduce energy consumption, resulting in reduced demand for fossil fuels and lower carbon emissions. Additionally, LED luminaires do not contain harmful substances like mercury, reducing environmental pollution and health risks.
Short payback period: The highluminous efficacy of LED luminaires means that lighting requirements can be met with lower wattage. Their energy-saving characteristics make LED luminaires widely used in Energy Performance Contract (EPC) projects. It helps municipal authorities or project owners to allocate the saved electricity costs for upfront investments, and the high light efficiency significantly shortens the payback period.
Strategies for improving luminous efficacy
LED driver efficiency
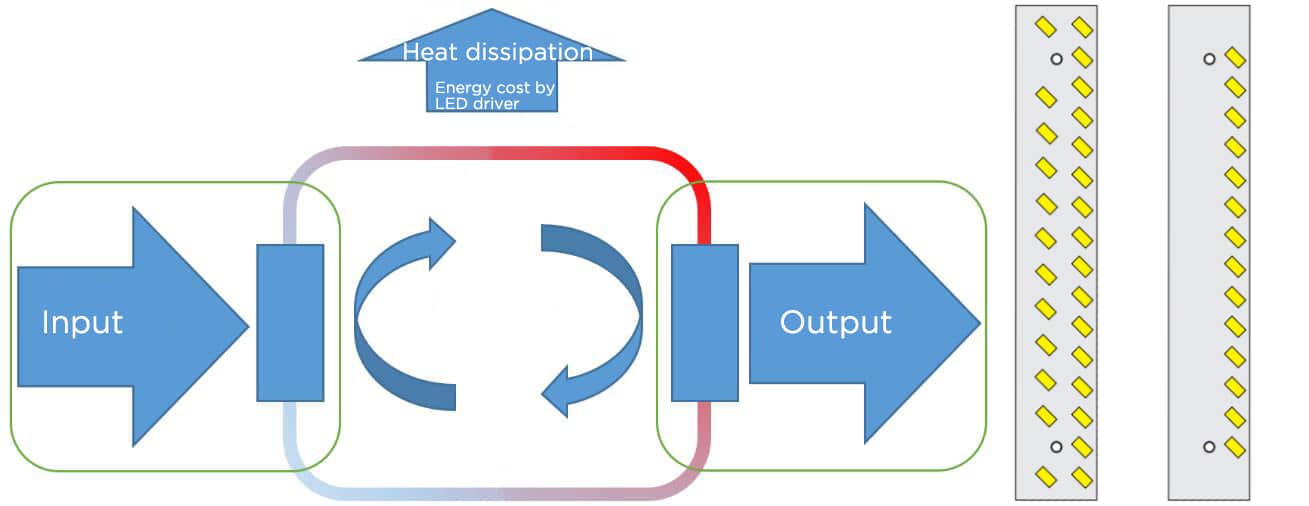
The main benefit of using a high-efficiency LED driver is energy saving, and the energy saved by a high-efficiency driver is quite important throughout the life cycle of the LED power supply. A 90% efficient drive dissipates almost half the power that an 80% efficient drive dissipates, so the savings in energy use over a long 50,000 hour lifetime can become significant. The higher the efficiency of the LED power supply, the higher the ratio between output and input, that is, more electric energy will be converted into light energy by the LED chips, as shown in the figure below.
In addition, for LED drivers, the biggest challenge may not be efficiency but reliability. Improving driver reliability, which is the weakest link among all components in a luminaire, poses a significant challenge, including fundamental reliability limitations of many driver subcomponents. Exploring the integration of solid-state components into drivers as a more reliable alternative should be considered, as solid-state drivers can simplify the parts count and reduce failures. Furthermore, high-efficiency drivers have lower heat loss and temperatures, which can significantly increase the product lifespan. Higher heat in less efficient drivers considerably raises component temperature and, to a lesser extent, failure rates.
Efficiency of LED chips
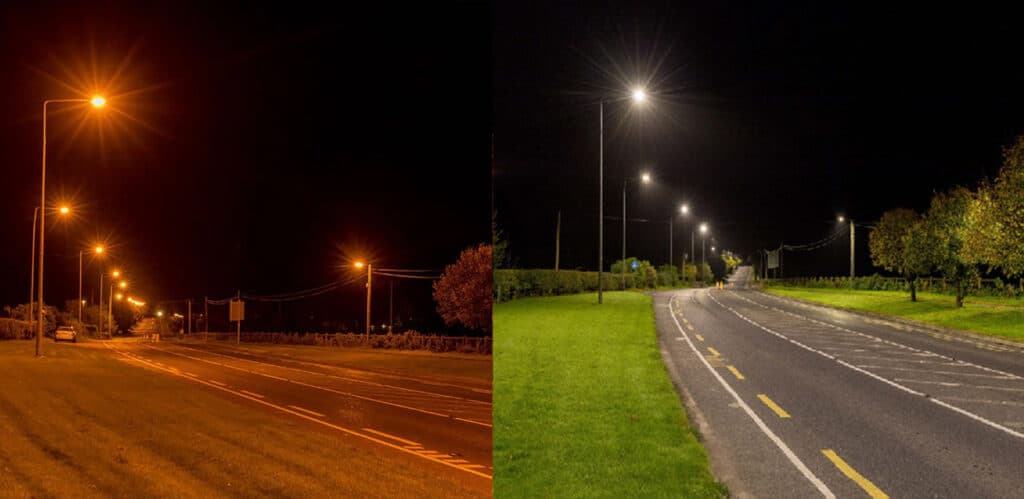
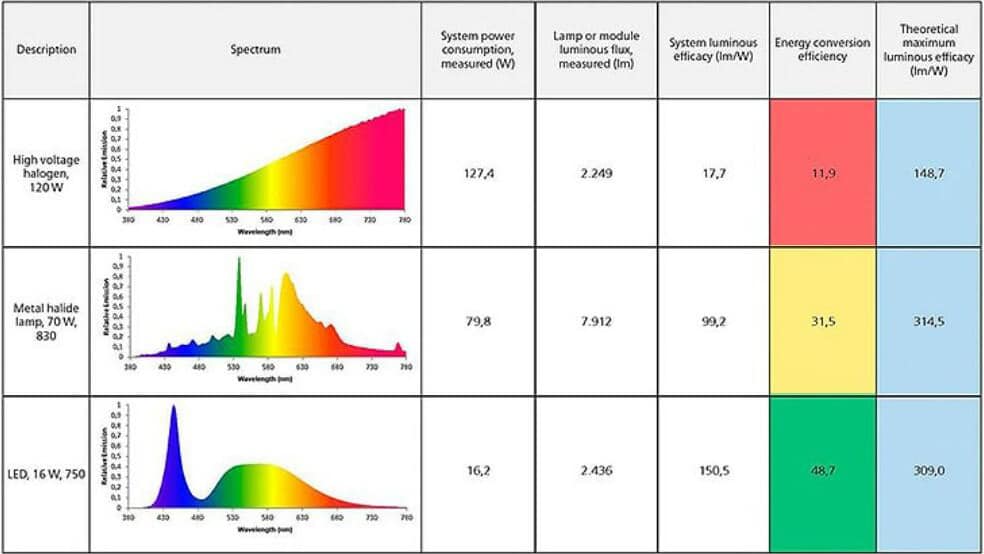
LED (Light Emitting Diode) technology is inherently more energy efficient than traditional lighting technologies such as High Pressure Sodium (HPS) or Metal Halide (MH). LEDs convert a higher percentage of electrical energy into visible light, minimizing wasted heat. LED technology itself still has a lot of room for improvement. Different qualities and types of LED chips have different efficiencies in converting electrical energy into light energy. Using LEDs with high luminous flux or efficacy helps to improve the efficiency of the luminaire. In addition, if LEDs with higher luminous flux cannot be used, the light efficiency can be improved by increasing the number of LEDs. When the driving current of the power supply is constant, the number of LEDs increases, the power remains unchanged, the driving current of a single LED decreases, the luminous flux of the LED increases, and the luminous efficacy of the LED increases. In addition, the difference in the color temperature and display index of the LEDs also has a certain impact on the light effect of the lamp bead. For details, please refer to the specification of the LED chips supplier. The following is not a comparison of the efficiency of different lighting technologies and LED chips in converting electrical energy into light energy.
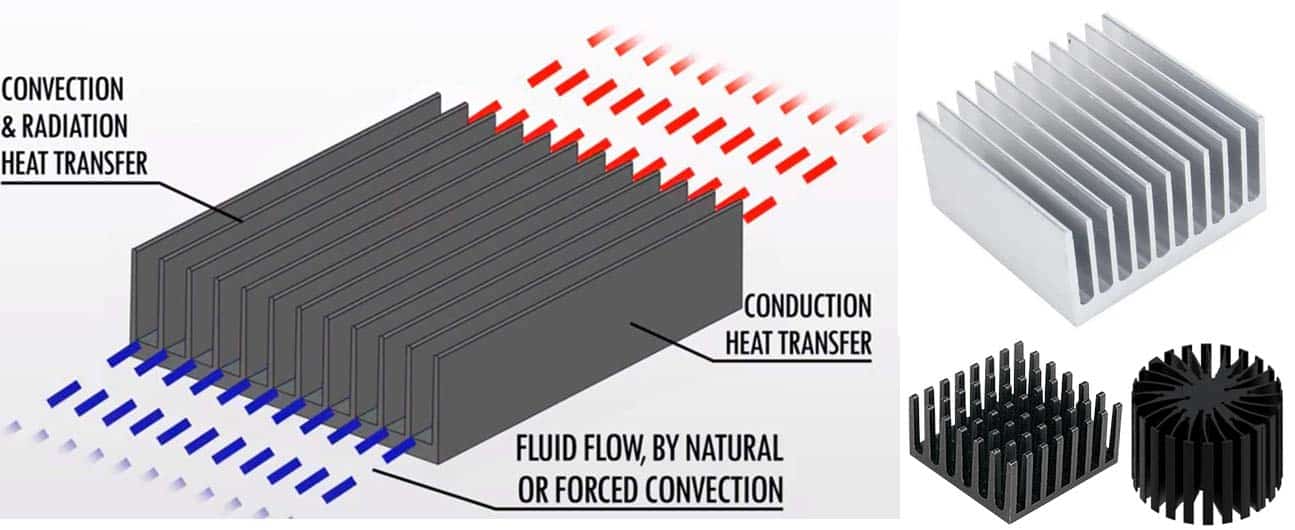
Heatsink – heat dissipation
The efficiency of LED lamps is related to its temperature. Generally speaking, the lower the temperature (within a reasonable range), the higher the efficiency of the lamp. On the contrary, the higher the temperature, the lower the lamp efficiency. LED thermal droop is a phenomenon in which the luminous efficiency of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) decreases with increasing temperature. This manifests itself in that when an LED heats up, it becomes less efficient at converting electrical energy into light, resulting in reduced light output. Some researchers believe this phenomenon is caused by the recombination of electron-hole pairs in the active region of the LED, thereby generating heat. As the temperature of the LED increases, the number of electron-hole pairs increases, resulting in increased heat generation, which will lead to a decrease in the quantum efficiency of the LED. The actual reason may be more complicated, but we just need to remember that the efficiency of the LED will decrease as the temperature increases.
Controlling the working temperature of the LED means ensuring that the working temperature of the LED is always within an appropriate range. Increasing the current increases light output, but it also increases heat. On the contrary, when we use a lower drive current in the design of LED lamps, the heat increase will not be so obvious, so as to avoid excessive temperature, reduce light decay and prolong the life of LED. At the same time, the lower drive current is also very helpful to improve the efficiency of the LED lamp itself. But we need to pay attention, lower drive current means we need to use more LEDs to achieve the design wattage of the lamp. To achieve effective heat dissipation and improve overall heat dissipation performance, LED street lamps can rely on external radiators to reduce the internal temperature and maintain a relatively balanced internal environment. By utilizing external radiators, the excess heat generated by the LED street lamp can be efficiently dissipated. This approach helps prevent overheating and ensures optimal functioning of the lamp. We list different heat sinks in the figure below. Depending on the effective connection between the PCB and the heat sink, we can improve the heat dissipation performance of the lamp and ensure that the LED chips work at a reasonable temperature.
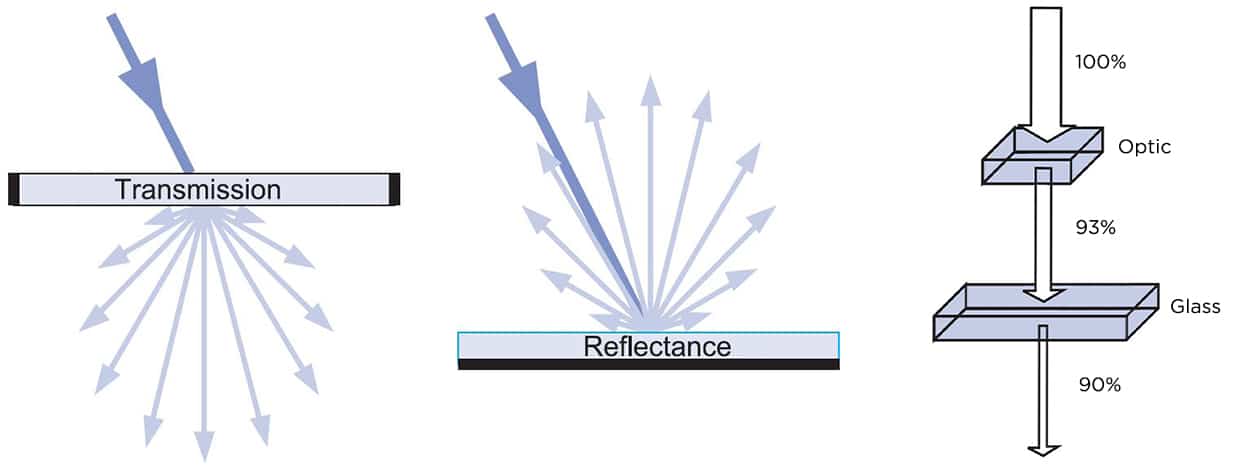
Optic
The optical system in the luminaire controls and manipulates the intensity and spatial distribution of the applied light. Various arrangements of lenses, reflectors and diffusers can be used depending on the lighting application, desired light distribution and form factor of the lighting product. Studies confirm that improved optical control can often use less total light to achieve specified illuminance levels. For outdoor applications (LED street lighting, flood lighting), proper light distribution can reduce over-illumination and unwanted, off-target lighting that manifests as light trespass or glare that is emitted into the atmosphere and causes the sky to glow.
In current applications, well-designed luminaires can experience less than 10% optical loss. Generally speaking, the fewer and smaller the LED package, the smaller the tip, and the more efficient the optical system. The number of layers of the lens, generally speaking, the more media (lenses and glass) the light passes through, the higher the loss. In addition, the material of the lens, the use of reflectors and diffusers also have an impact on the luminous efficacy. For example, the light transmittance of the LED lens made of PC is lower than that of the lens made of PMMA.
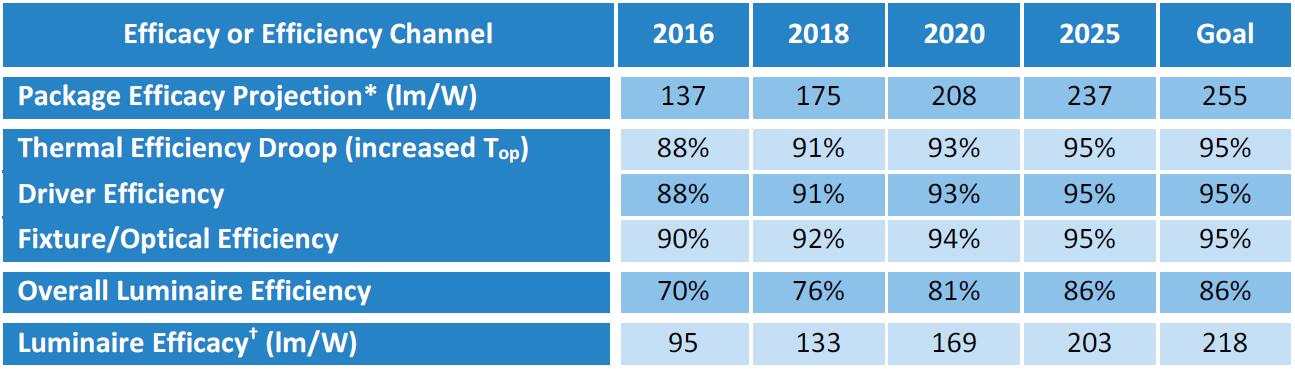
Trends in Luminous Efficacy of LED Luminaires
As follows, I list the luminous efficacy of LED chips in different periods, as well as power efficiency, lens light transmittance, and the impact of these on the luminaire’s luminous efficacy. With the advancement of technology, we believe that the light efficiency of LED lamps can be further improved in the future.
ZGSM LED street light with different luminous efficacy
Since its establishment in 2005, ZGSM has been committed to the development of high-efficiency LED lamps. At present, our company has made good progress in the development of LED street lamps. Below we list ZGSM LED street lights with different luminous efficacy in different periods.
- ZGSM D2 series
- Developed on 2009
- CE certificated
- Unavailbale, continued by H series
- ZGSM H series
- Developed on 2013
- CE and ULcertificated
- Module design with UL certificate
- ZGSM K series
- Developed on 2016
- CE, ENEC certificated
- Full die-casting auminium
- ZGSM Rifle series
- Developed on 2020
- CE, ENEC+ certificated
- Tool-less design with full sets of certificates
- ZGSM Falcon series
- Developed on 2022
- CE, ENEC certificated
- ZGSM new generation 20th street light
Summary
This article mainly describes the advantages of high-efficiency LED lamps and how to improve the light efficiency of LED lamps. High-efficiency LED lamps have the advantages of energy saving, environmental protection and lower operating costs. They can produce the same or brighter lighting effects with less electricity, reduce energy consumption, reduce electricity bills, and play a positive role in environmental protection and carbon emission reduction. In the application of solar street lights, high light efficiency can also extend battery life. In order to improve the luminous efficacy of LED lamps, we can choose high-efficiency LED chips and driving power, optimize heat dissipation design and optical design, etc. Of course, the methods are not limited to these. High-efficiency LED lamps make it a sustainable and economical lighting solution. More and more manufacturers are committed to research in this area, and buyers and project parties also prefer such solutions because they are energy-saving and environmentally friendly.
Rated Products
Related Blogs
Related Cases
People also ask
Author introduction

Hello Customers,
My name is Taylor Gong, I’m the product manager of ZGSM Tech. I have been in the LED lights industry for more than 13 years. Good at lighting design, street light system configuration, and bidding technology support. Feel free to contact us. I’m happy to provide you with the best service and products.
Email: [email protected] | WhatsApp: +8615068758483